EEG/EMG based speech decoding for patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Decoding imagined speech from neural signals for communication restoration
Decoding Imagined Speech for ALS Communication
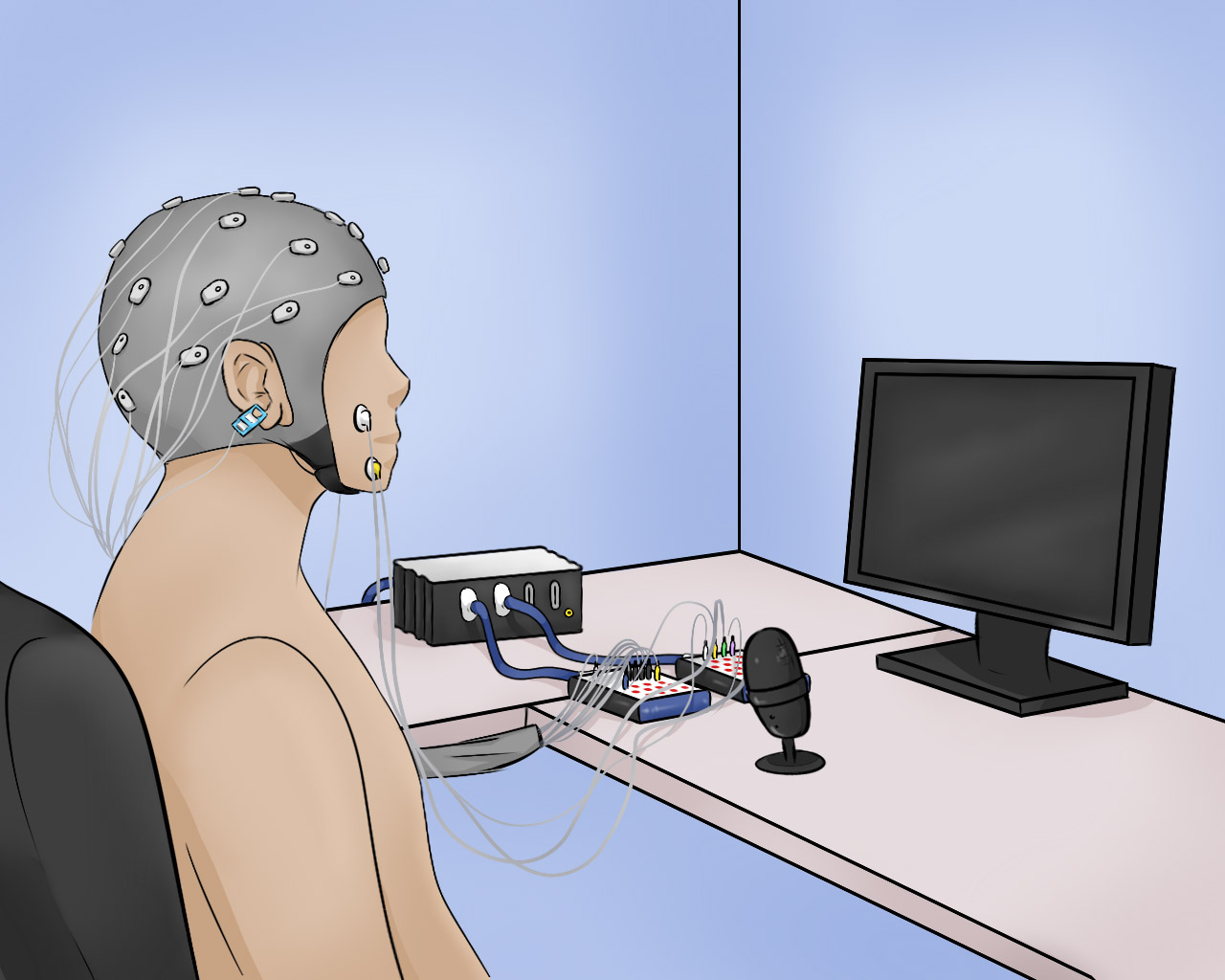
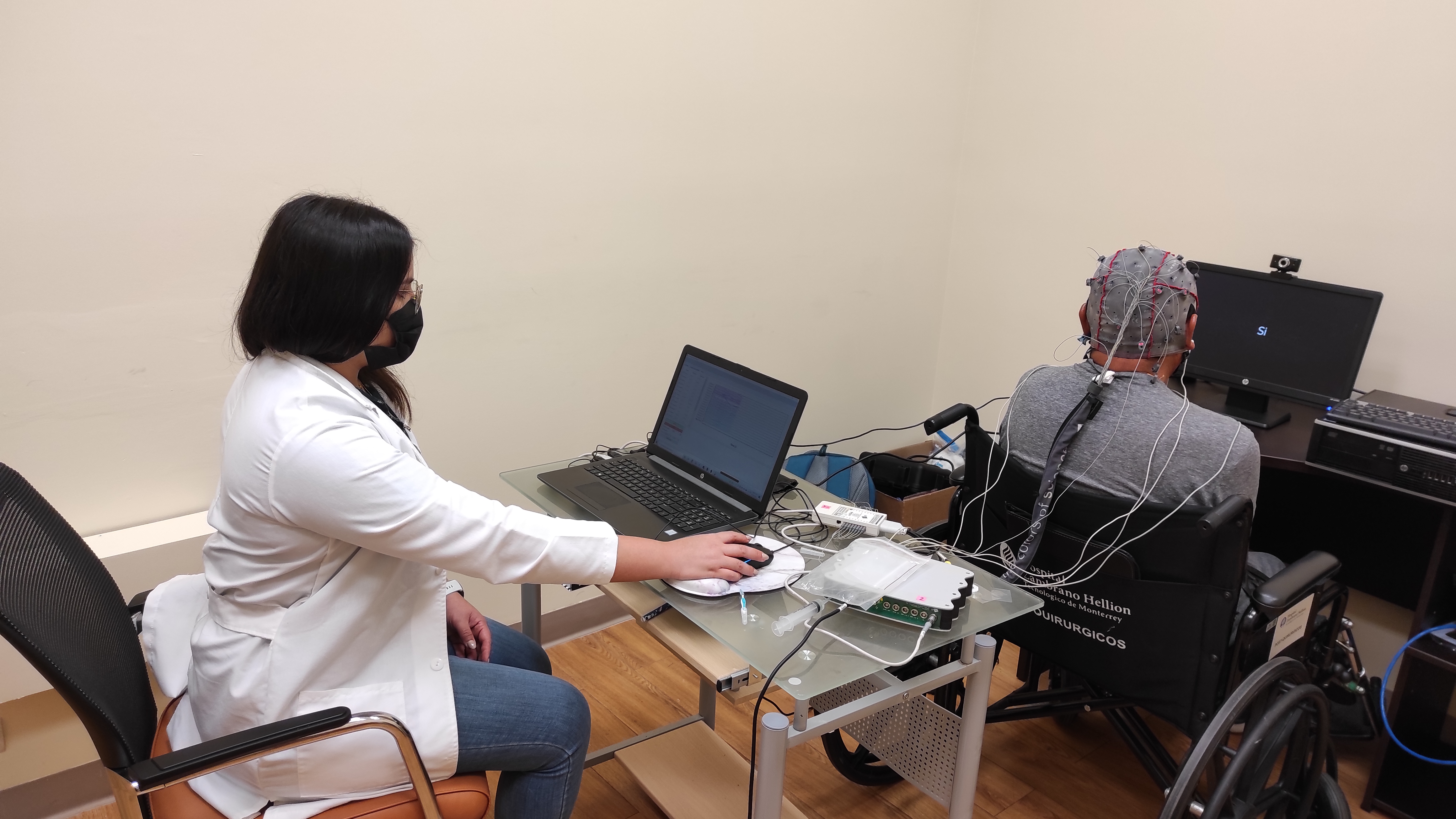
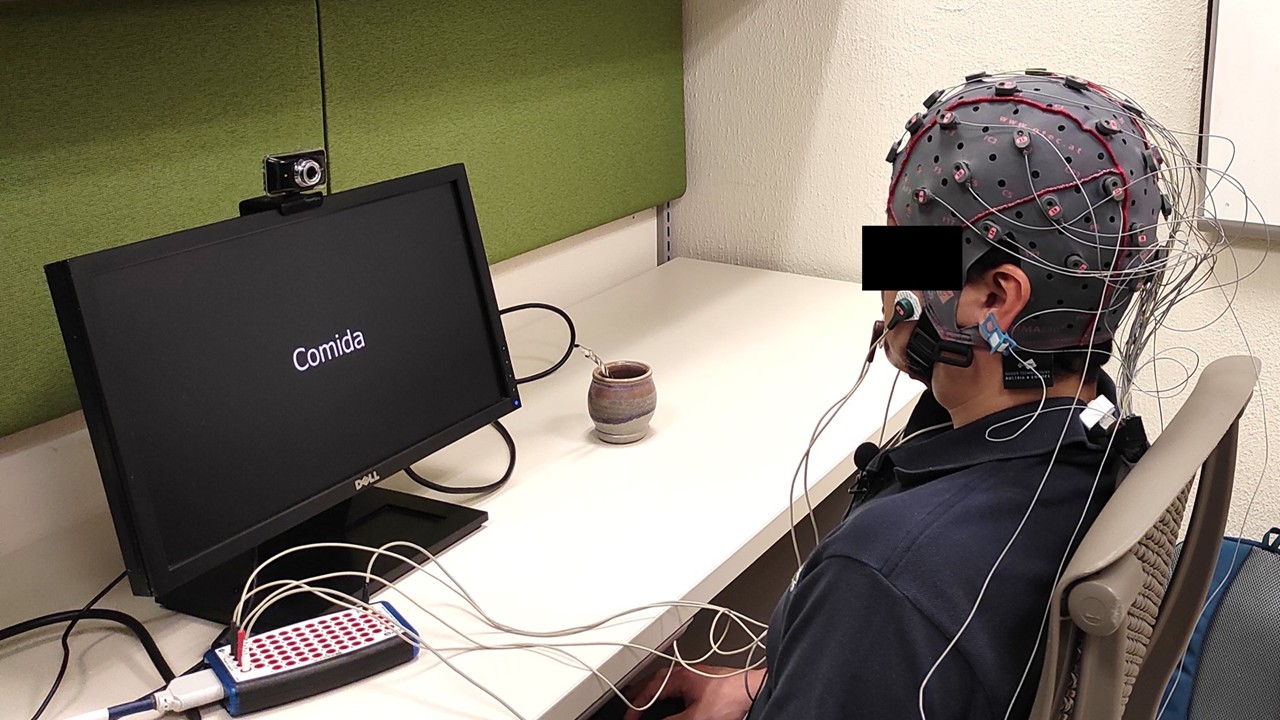
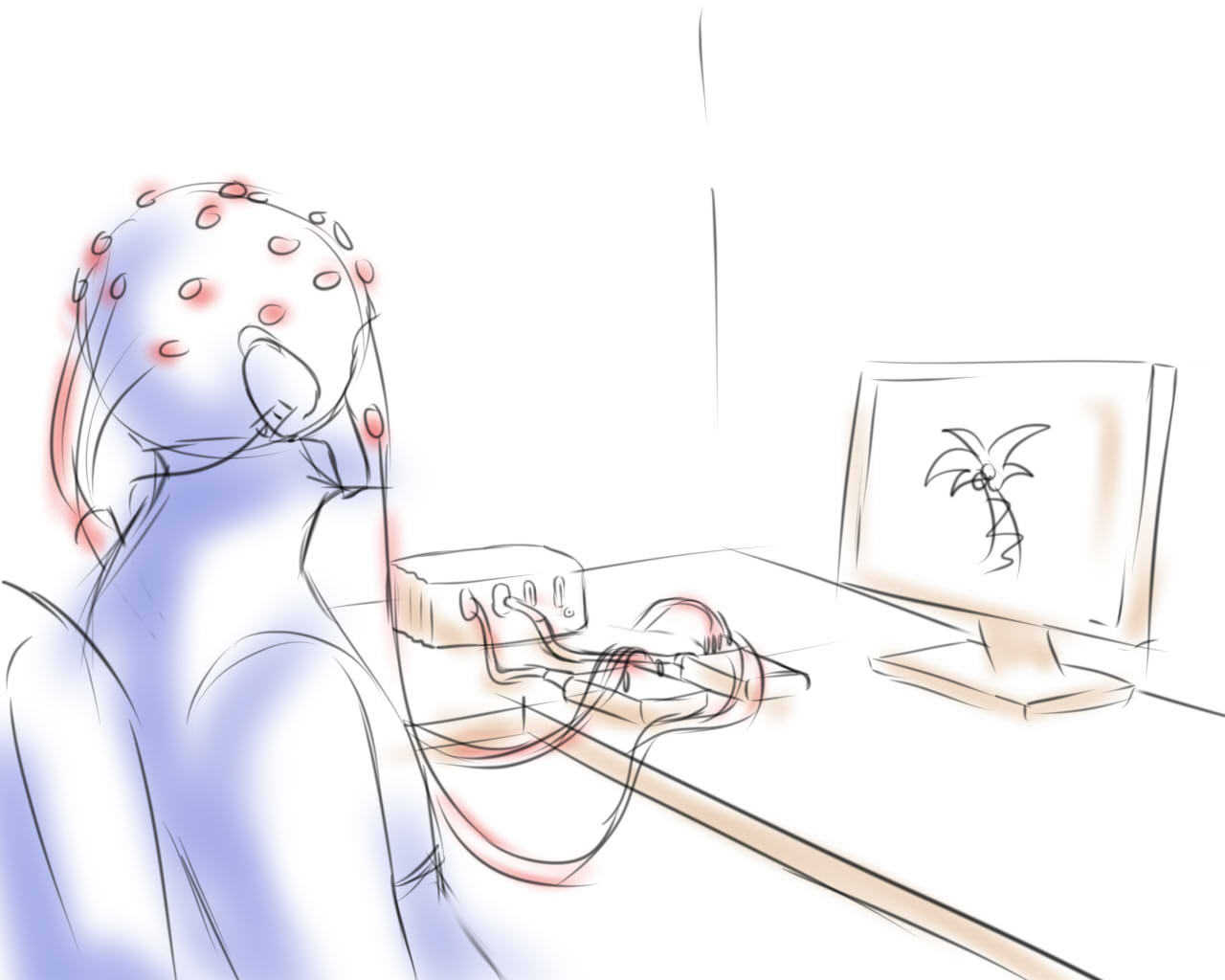
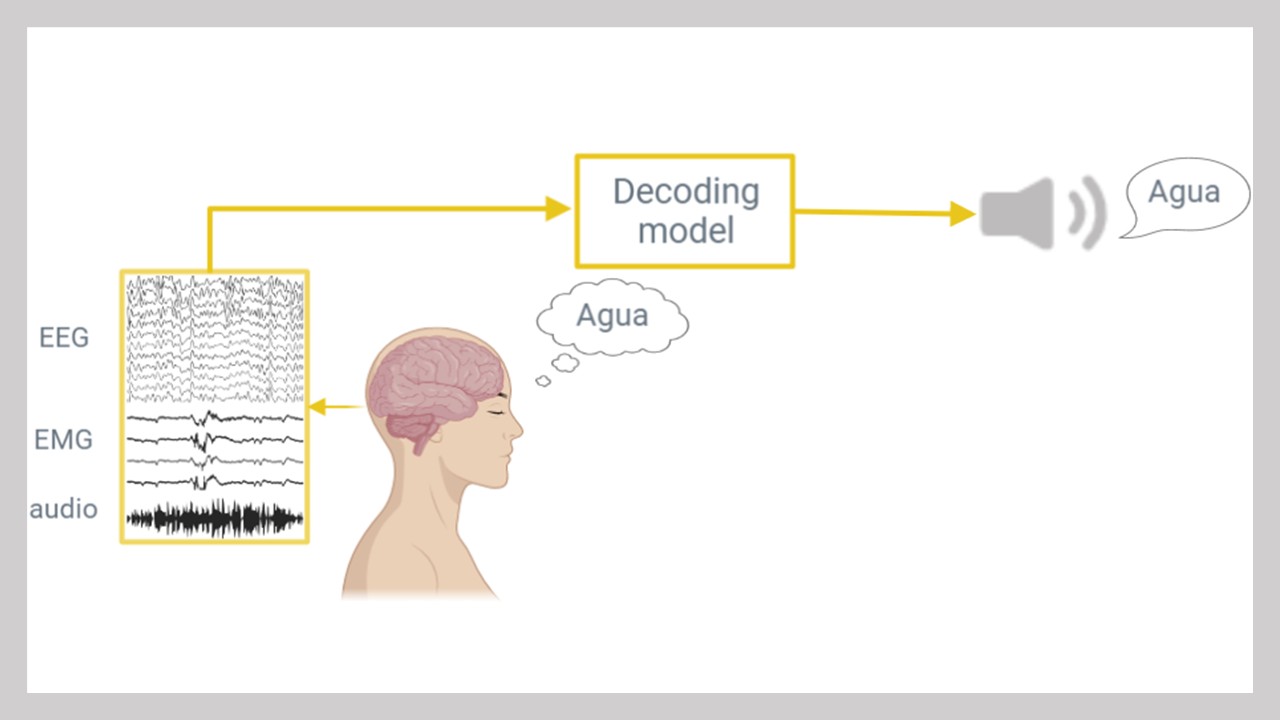
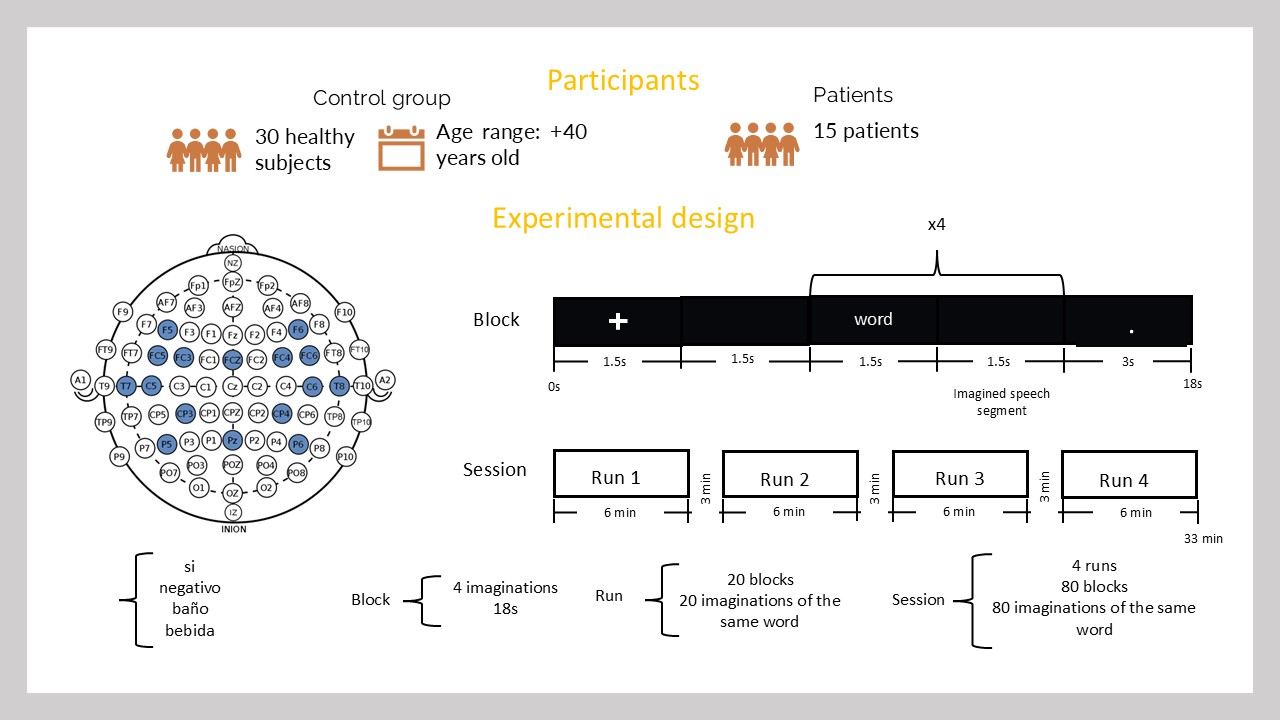
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) lead to the loss of motor skills and, in many cases, the inability to speak. Motivated by this situation, this project addresses the decoding of imagined speech words (internally pronouncing the word without emitting any sound or gesture) directly from EEG and facial EMG signals. We conducted experiments where participants pronounced, imagined, and mentally read various words differing in connotation, syllable count, grammatical class, semantic meaning, and functional role within a sentence. The recorded datasets have been used to investigate the recognition of intra-subject and inter-subject classification scenarios, including word vs. word, short vs. long words, multi-class, and other tasks, in both healthy participants and ALS patients.
Research Focus
-
Speech Types:
- Overt speech
- Imagined speech
- Mental reading
- Signal Types: EEG and facial EMG
-
Classification Tasks:
- Word vs. word
- Short vs. long words
- Multi-class
- Population: Healthy and ALS patients
Project Highlights
- Technology: EEG/EMG Signal Processing
- Application: ALS Communication Restoration
- Key Feature: Imagined Speech Decoding
Technical Details
System Components
- EEG/EMG Acquisition System
- Speech Paradigm Design
- Machine Learning Classifiers
- Grammatical Class Analyzer