P300-based BCI coupled with a robotic hand-orthosis for individual finger movements
Brain-controlled assistive device for ALS patients
P300-based BCI for Robotic Hand-Orthosis Control
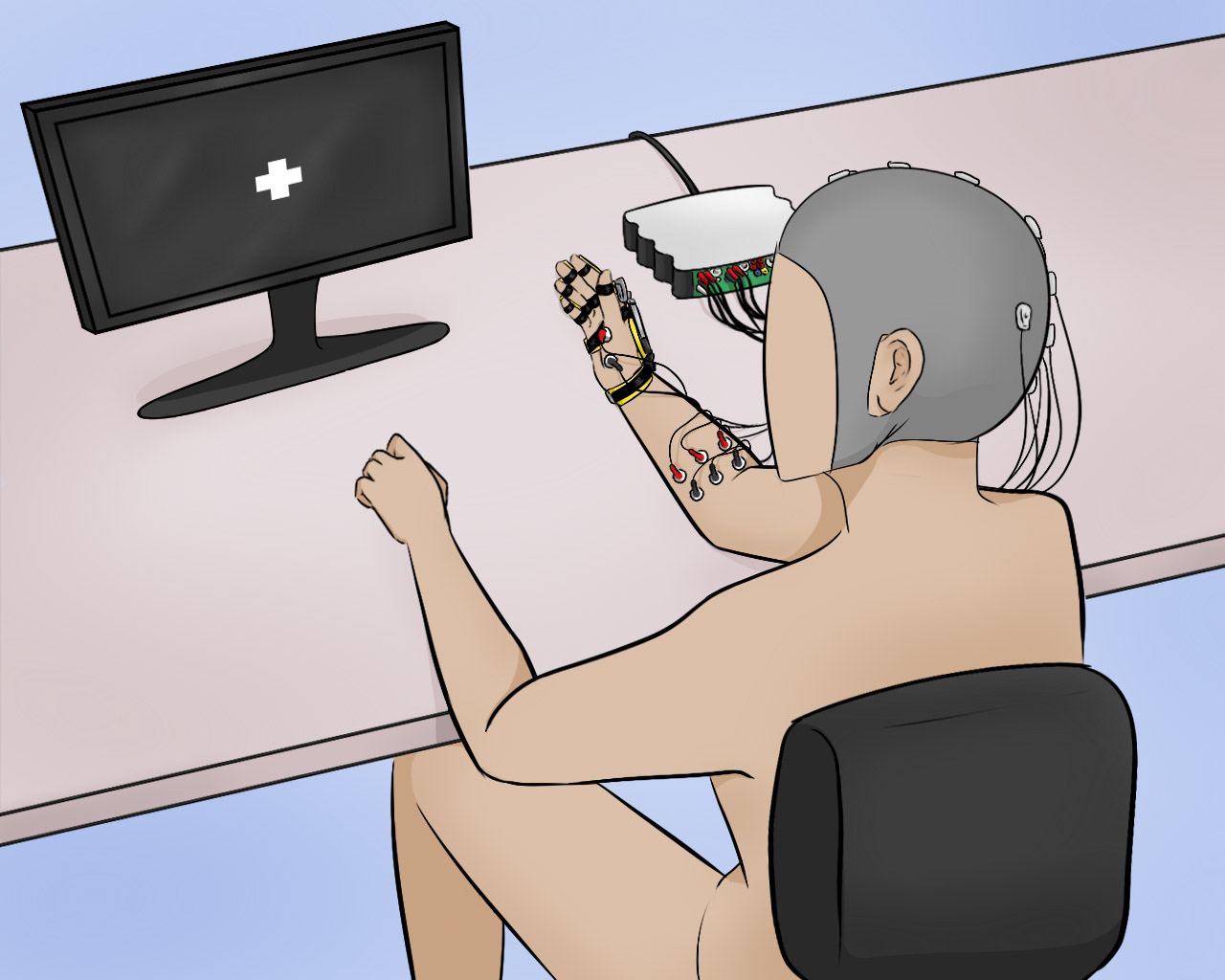
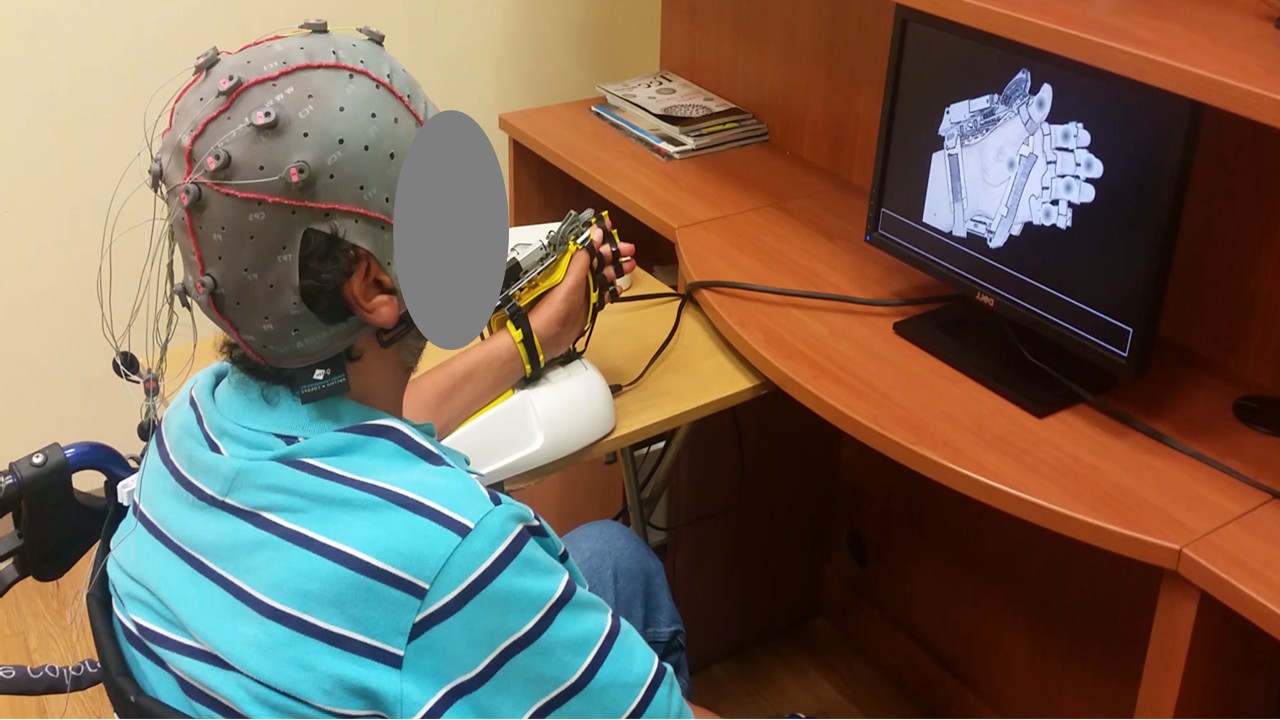
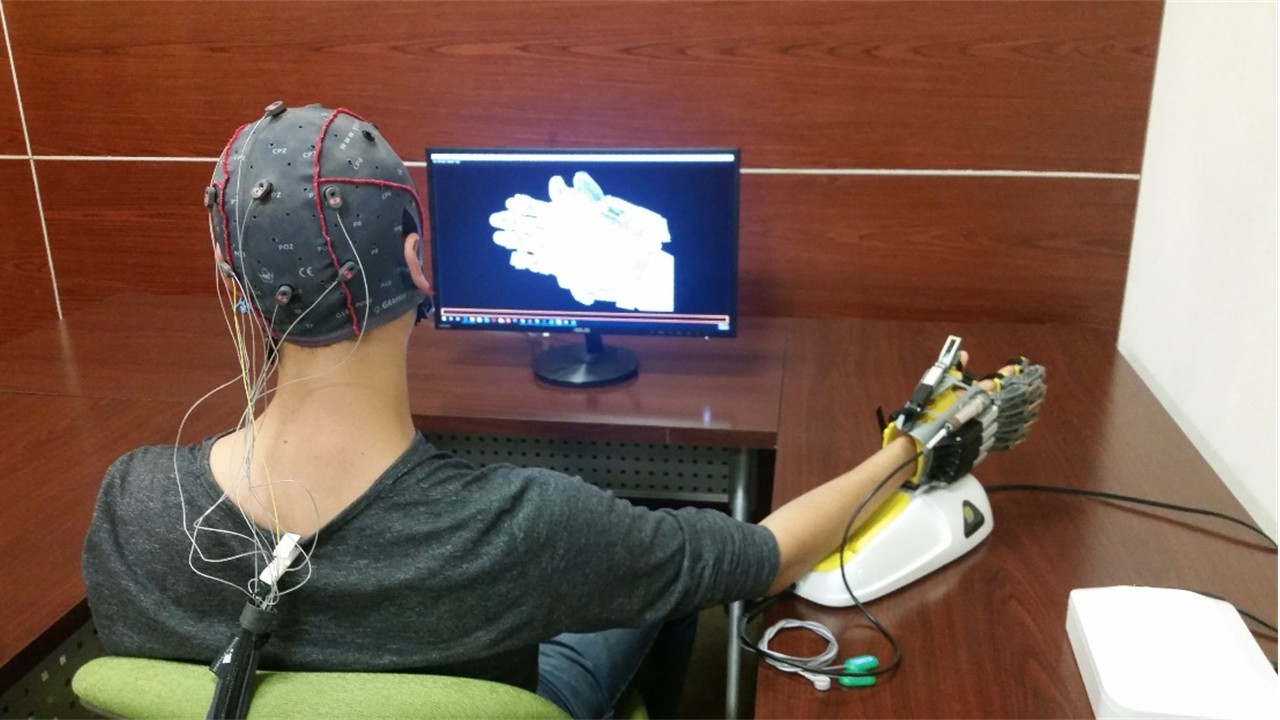
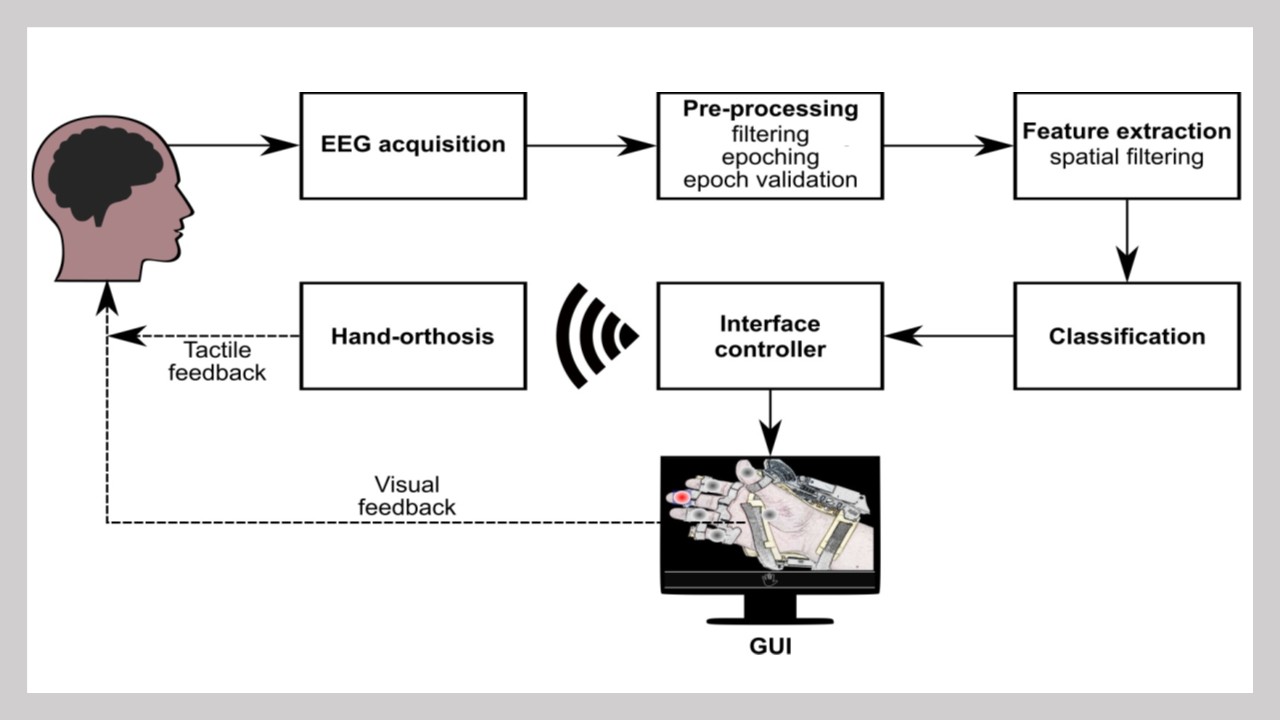
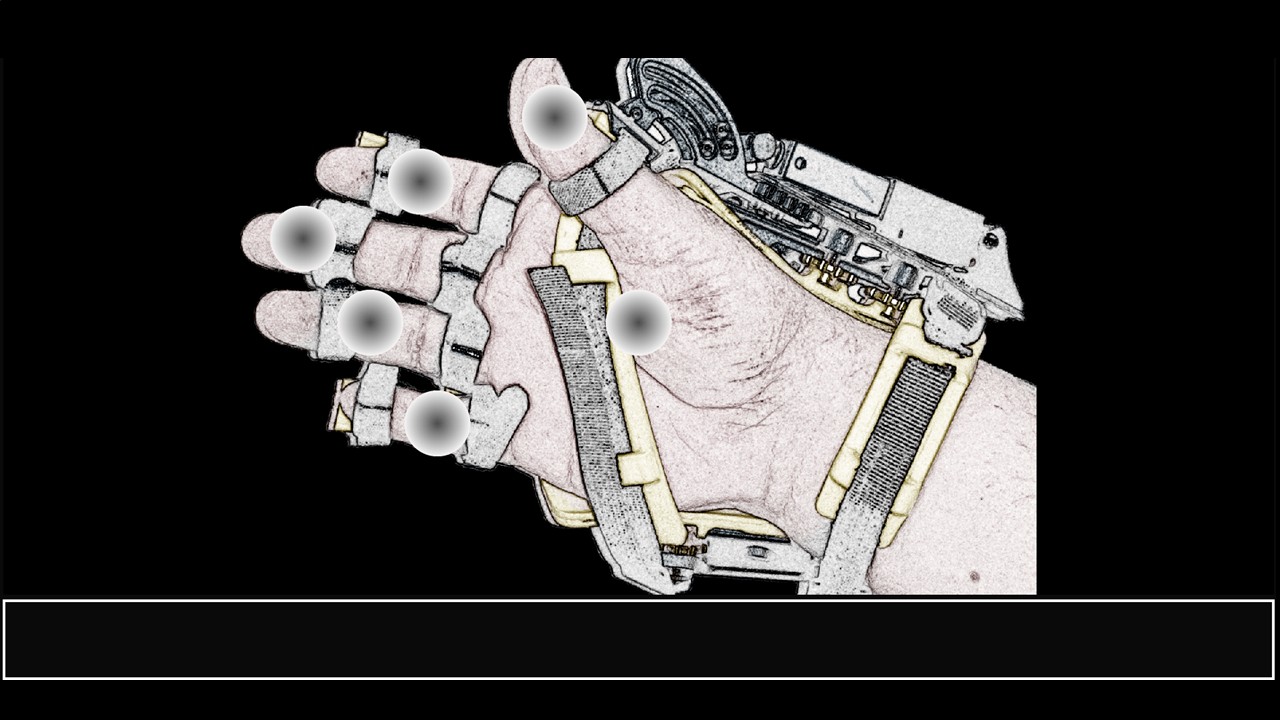
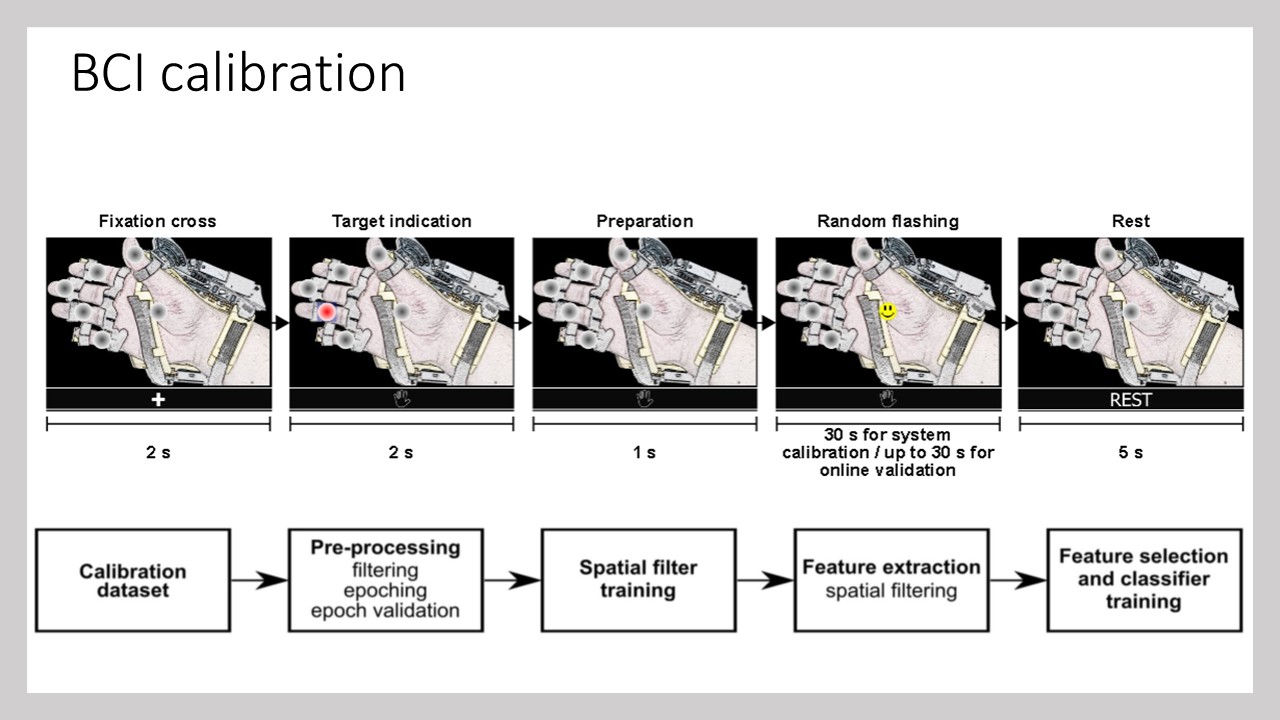
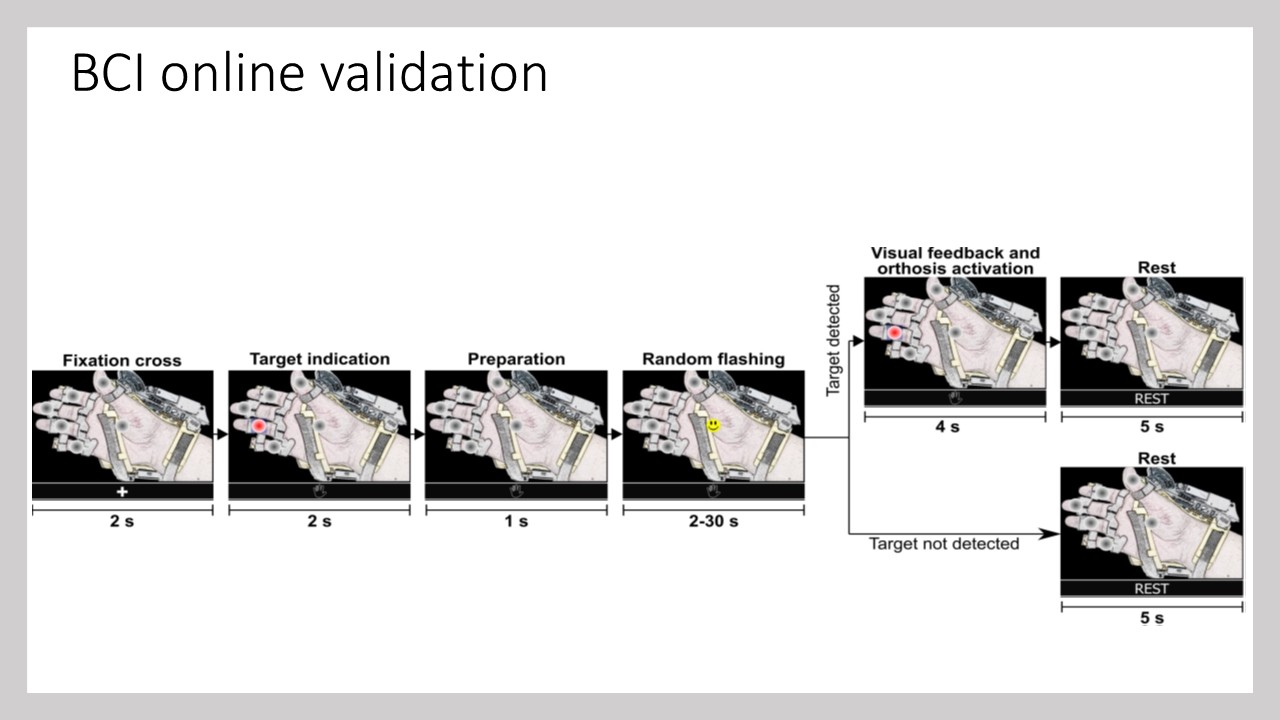
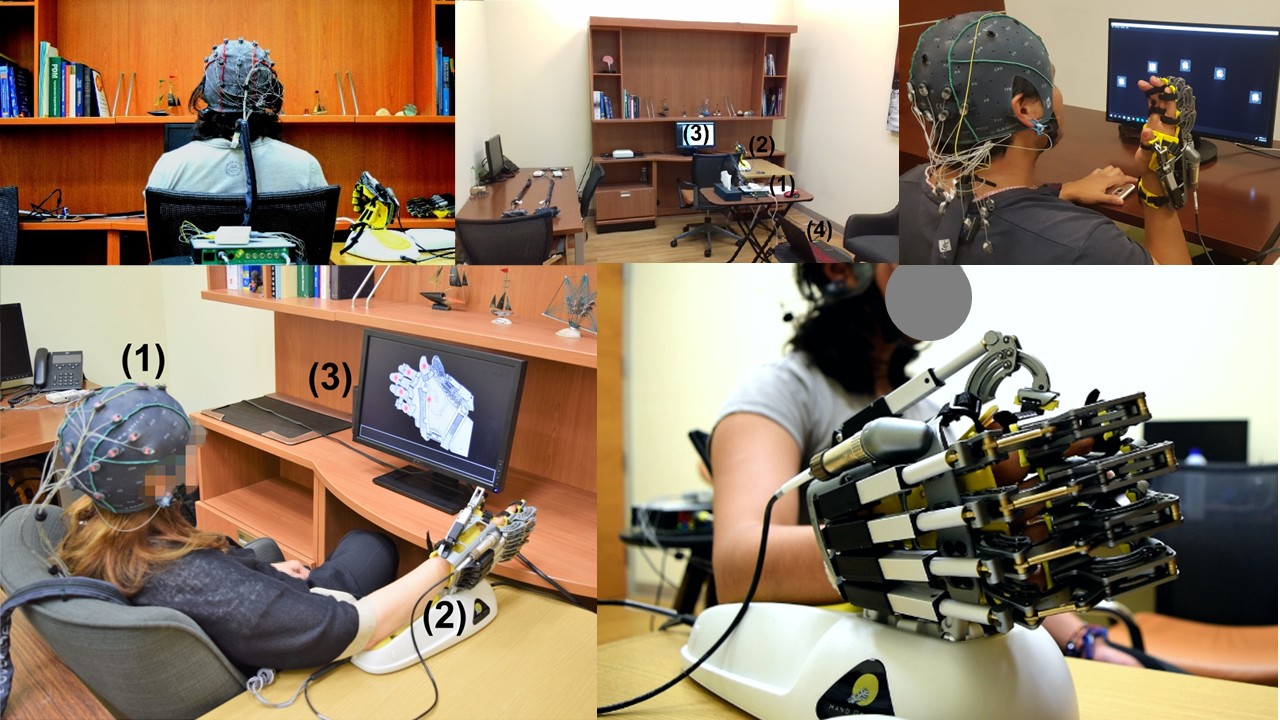
This project involved the design, implementation, and evaluation of a P300-based BCI to control a robotic hand-orthosis. The system aims to assist patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) who are unable to open and close their hands independently. The BCI interface allows users to select one of six targets representing different finger movements. These targets enable the flexion-extension of each finger individually or the simultaneous movement of all five fingers. In our implementation, the BCI system consisted of six options: individual flexion-extension of each finger and simultaneous flexion-extension of all fingers. Visual indicators included five gray circles placed over the fingers to represent individual movements and a circle over the palm to indicate the hand opening and closing. The system was tested both offline and online with eighteen healthy subjects and eight ALS patients to assess its effectiveness.
System Functionality
- P300 Detection: EEG-based detection of target selection
-
Finger Control:
- 5 options for individual finger movements
- 1 option for full hand movement
- Visual Interface: Gray circles over fingers and palm
- Clinical Testing: Evaluated with 18 healthy subjects and 8 ALS patients
Project Highlights
- Technology: P300-BCI + Robotic Orthosis
- Application: ALS patient assistance
- Key Feature: Individual finger control
Technical Details
System Components
- P300-BCI System
- Robotic Hand-Orthosis
- Visual Stimulation Interface
- Signal Processing Unit